
Complementary angle theoremĪccording to the complementary angle theorem, if two angles are complementary to the same angle, they are congruent. Putting this into an equation, if A and B are two angles, then A + B = 180°. It is not necessary for the two angles to be contiguous their aggregate must equal 180°. Consequently, the complementary angles are referred to as complementary. Two angles are referred to as supplementary angles if their sum equals 180°.
#Example of a supplementary angle plus#
Putting this into an equation, if C and D are two angles, then C plus D equals 90°. Nevertheless, their aggregate must equal 90°. Again, the two angles need not be contiguous in this instance. These angles are considered complementary to one another. Two angles are considered complementary if their sum is equal to 90°, or a right angle. Definition of Complementary and Supplementary Angles When the measurement of an angle equals 360°, the angle is considered complete. Since a right angle has a measure of 180°, it is half of a complete revolution of a circle.Ī reflex angle has a measure of more than 180° but less than 360°. A straight angle consists of two right angles. At a right angle, the two beams are perpendicular to one another. In other words, a right angle is a straight line, and the angle generated by two rays equals 180°. When an angle’s measurement is less than 180° but greater than 90°, it is obtuse.Ī straight angle refers to the angle formed by a straight line. Because it resembles the letter L, a right angle is instantly identifiable. When an angle is 90°, it is referred to as a right angle. Let us read about each sort of angle and its attributes separately.Īcute angles have a measure greater than 0° and less than 90°. On the basis of angle measurement, each type of angle has a distinct identifier. Engineers and architects employ angles while designing highways, buildings, and athletic facilities.
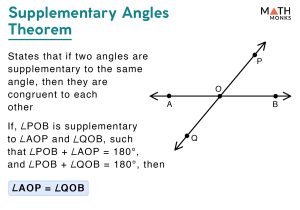
Angles are an integral component of our daily lives. Typically, angles are measured in degrees and radians, a unit of circularity or rotation. An ‘angle’ is the measurement of the ‘opening’ between these two rays. Definition of anglesĪngles are created when two lines meet at a single point. For instance, if two angles measure 110° and 70°, they can be considered complementary angles because their sum equals 180°. By combining complementary angles together, right angles can be produced. When the total of two angles equals exactly 180°, they are referred to as supplementary angles. For instance, two angles measuring 65° and 25° are complementary since their sum is exactly 90°. When two complementary angles are adjacent, a right angle is created. The primary distinction between a complementary angle and a supplementary angle is that the sum of the two angles that comprise a complementary angle is 90°, but the total of the two angles that comprise a supplementary angle is 180°.Ĭomplementary angles are generated when the total of two angles equals precisely 90 °.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
